Back to recipes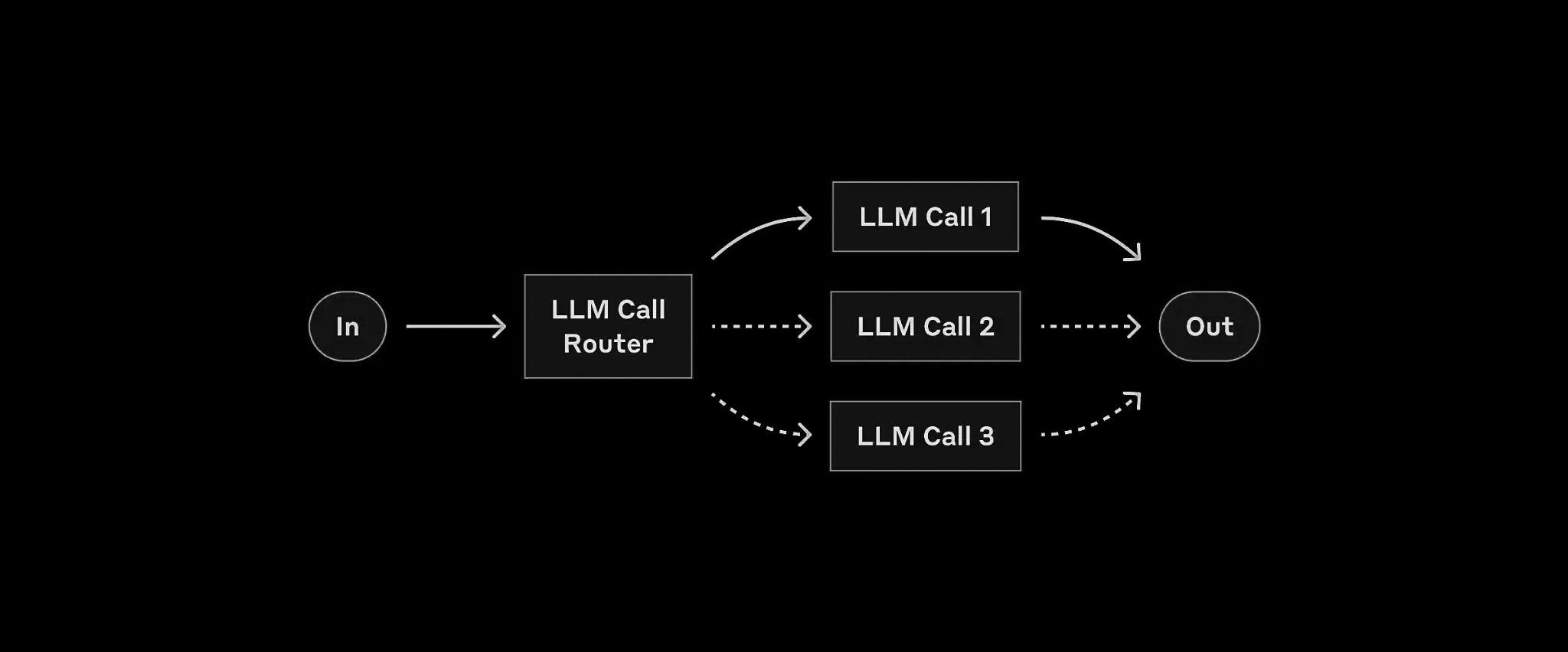
Routing
Low Latency
Routing is an efficient workflow designed to direct inputs to the most appropriate LLM or processing pipeline based on the nature of the task. This approach optimizes performance by ensuring that each query is handled by the most suitable model or process.

Diagram Explanation
The diagram illustrates the routing process. At the top, we have the input, which is first analyzed by a classifier. Based on the classification result, the input is then directed to one of several specialized LLMs or processes. Each path is optimized for a specific type of task, ensuring efficient and accurate processing.
Use Cases
- Customer Support Triage: Automatically categorize and route customer inquiries to the appropriate department.
- Multi-lingual Processing: Route text to language-specific models for translation or analysis based on detected language.
- Complexity-based Model Selection: Direct simple queries to faster, smaller models and complex queries to more powerful models.
Implementation
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import Literal, Dict
from helpers import run_llm, JSON_llm
def router_workflow(input_query: str, routes: Dict[str, str]) -> str:
"""Given a `input_query` and a dictionary of `routes` containing options and details for each.
Selects the best model for the task and return the response from the model.
"""
ROUTER_PROMPT = """Given a user prompt/query: {user_query}, select the best option out of the following routes:
{routes}. Answer only in JSON format."""
# Create a schema from the routes dictionary
class Schema(BaseModel):
route: Literal[tuple(routes.keys())]
reason: str = Field(
description="Short one-liner explanation why this route was selected for the task in the prompt/query."
)
# Call LLM to select route
selected_route = JSON_llm(
ROUTER_PROMPT.format(user_query=input_query, routes=routes), Schema
)
print(
f"Selected route:{selected_route['route']}\nReason: {selected_route['reason']}\n"
)
# Use LLM on selected route.
# Could also have different prompts that need to be used for each route.
response = run_llm(user_prompt=input_query, model=selected_route["route"])
print(f"Response: {response}\n")
return response
# Example usage
prompt_list = [
"Produce python snippet to check to see if a number is prime or not.",
"Plan and provide a short itenary for a 2 week vacation in Europe.",
"Write a short story about a dragon and a knight.",
]
model_routes = {
"Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct": "Best model choice for code generation tasks.",
"Gryphe/MythoMax-L2-13b": "Best model choice for story-telling, role-playing and fantasy tasks.",
"Qwen/QwQ-32B-Preview": "Best model for reasoning, planning and multi-step tasks",
}
for i, prompt in enumerate(prompt_list):
print(f"Task {i+1}: {prompt}\n")
print(20 * "==")
router_workflow(prompt, model_routes)